Weather and Climate: a Teachers’ Guide
Pathway: Extending Weather
Depressions – Microclimates – Urban Climates – Tropical Cyclones
Lesson overview: In this lesson we explore the structure, location and names for Tropical Cyclones as well as some of their potential impacts.
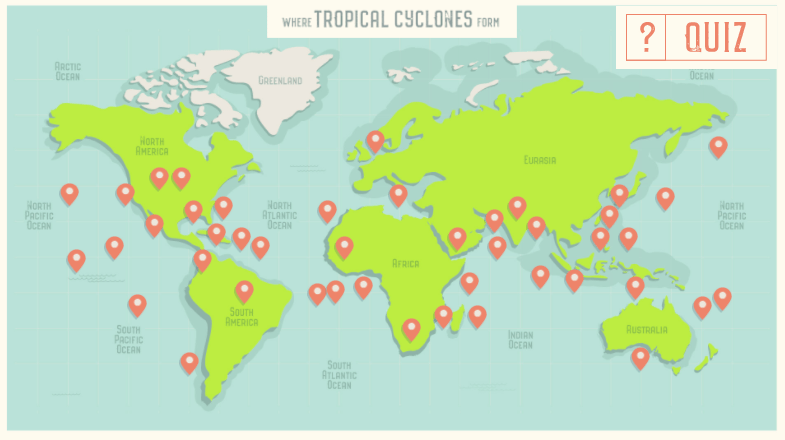
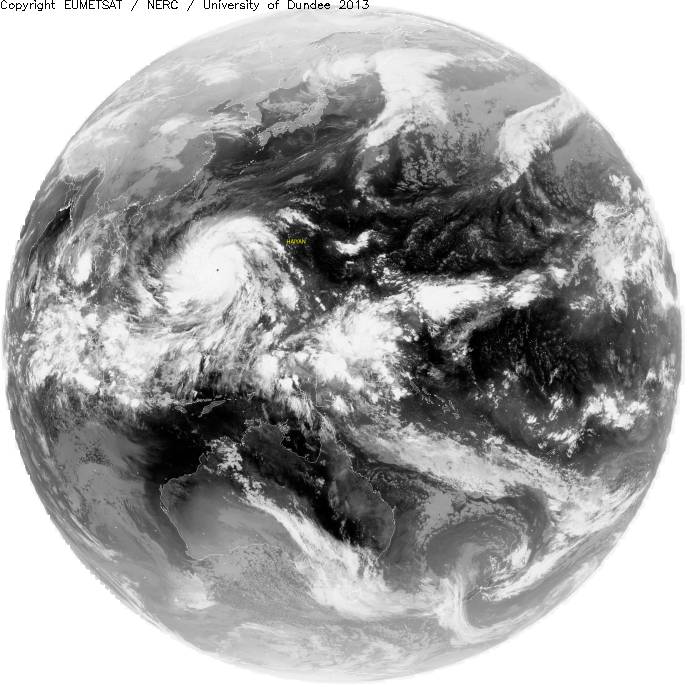
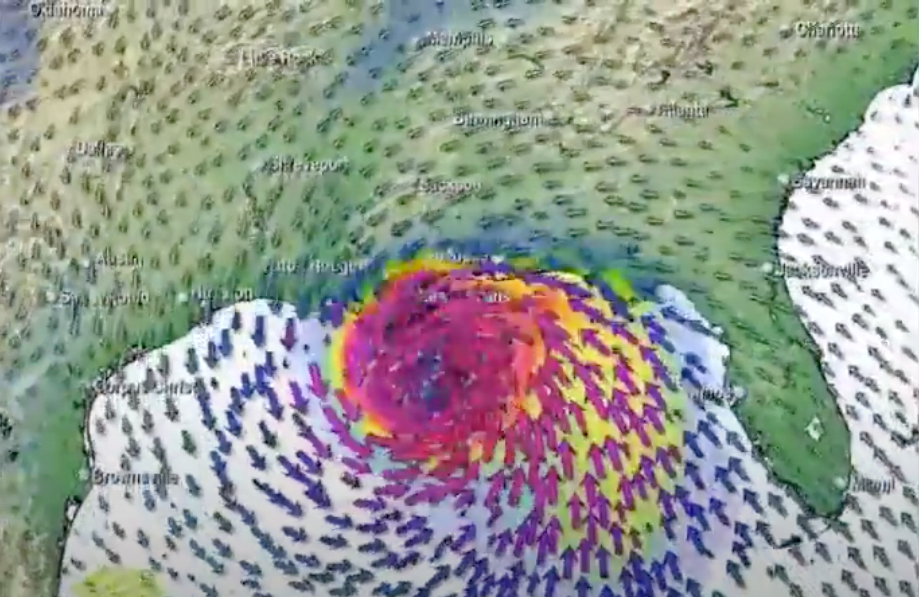
Tropical Cyclones are intense and extremely damaging storms. Fuelled by the transfer of heat from the ocean to the atmosphere they can grow into some of the most destructive weather systems on Earth. Tropical cyclones need specific conditions to form and intensify. These limit the locations in which Tropical Cyclones are able to form. Called Tropical Cyclones anywhere in the world, they are classified as Typhoons in the North-West Pacific and Hurricanes in the Atlantic and North-East Pacific. A Tropical Cyclone has a distinctive structure, consisting of a clear central ‘eye’, surrounded by extensive cloud bands that spiral outwards and may be hundreds of kilometres long. They can have severe impacts, causing coastal flooding and widespread damage to both the natural world and human infrastructure. As the climate changes, the most damaging Tropical Cyclones are expected to increase in intensity.
Learning objectives:
-
To understand what weather and hazards are associated with a Tropical Cyclone.
-
To be able to describe the structure of a Tropical Cyclone.
-
To be able to explain how and why Tropical Cyclones form.
Key Teaching Resources
Tropical Cyclones PowerPoint
Tropical Cyclones worksheet
Hurricane Dorian student data
Plotting Tropical Storm locations using GIS – video.
Teacher CPD/ Extended Reading
Read Tropical Cyclones_More for Teachers
or watch
Alternative or Extension Resources
Typhoon Haiyan GIS activity and background information
Tropical Cyclone challenge game
Further Tropical Cyclone teaching resources
A Hurricane is Approaching: a listening exercise based on a recent National Hurricane Center podcast.
Tropical storm tracker: grid reference plotting practice
Make a Tropical storm case study infographic using this basic template